We use cookies to make your experience better. To comply with the new e-Privacy directive, we need to ask for your consent to set the cookies. Learn more.

What is Creatine?
It is found in every muscle, providing high-intensity energy depending upon one’s own natural levels. If your level is low, it can be raised by taking Ultimate Nutrition Creatine.
Technically, creatine is a nitrogenous organic acid derived from three amino acids: L-arginine, L-glycine, and L-methionine. If you are asking what does creatine do, its main purpose is to provide immediate energy for the muscles (we’ll explain exactly how does creatine work later).
Creatine is essential for athletes, sportspeople, and bodybuilders because it increases their ability to produce energy. A normal diet may contain 1–2 g of creatine per day, meaning muscle creatine stores are only about 60–80% saturated. Therefore, supplementation serves to increase muscle creatine by up to 40%, which is one of the huge creatine benefits for any sportsperson. The most common and researched form you will find in supplements is creatine monohydrate.
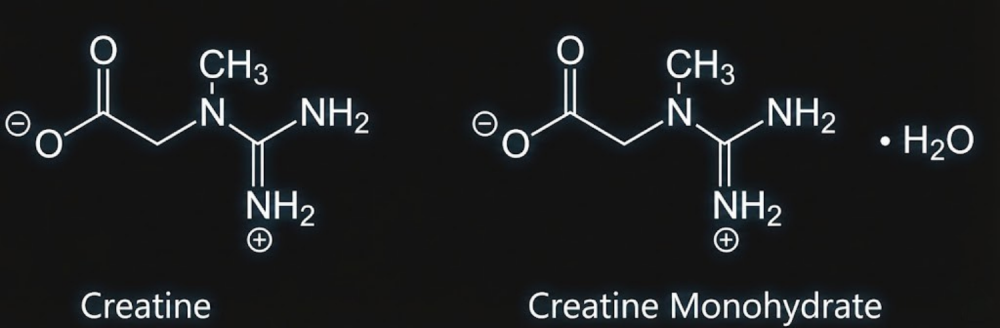
What is creatine monohydrate exactly? It is simply creatine attached to a water molecule, which makes it highly stable and easy for the body to absorb. The average 70kg person stores around 100-120g of creatine in their skeletal muscle, but this muscle has the capacity to store 160g. Ultimate Nutrition supplementation aims to feed and raise your natural levels, allowing the muscles to have a constant supply when needed for ATP re-synthesis.
As well as being produced naturally in the liver, we get creatine from protein-rich foods like meat and fish. However, for performance-enhancing benefits of creatine and to maximize stores in the muscles, you need to take it in supplement form. More creatine in the muscle store means you are maximizing your energy output.
How Does Creatine Work?
To understand how does creatine work, we must look at energy systems. The human body relies on three primary energy systems—phosphagen, glycolytic, and oxidative—to produce and utilize energy for various physical activities.
Your body utilizes these three main energy systems to generate ATP:
- The Glycolytic System (Short-term Energy)
- The ATP-PC System (Immediate Energy)
- The Oxidative System (Long-term Energy)
Glycolytic System (Anaerobic System): Short-term Energy.
Function: When the phosphagen system is depleted, the glycolytic system kicks in, breaking down glucose to produce ATP without the need for oxygen. This system is crucial for activities lasting from about 10 seconds to 2 minutes, such as a 400-meter sprint or high-intensity interval training (HIIT).
Phosphagen System (ATP-PC System): Immediate Energy.
Function: This system provides immediate energy for short, high-intensity activities, such as sprinting or heavy lifting. It relies on stored adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and phosphocreatine (PC) in the muscles.
Oxidative System (Aerobic System): Long-term Energy.
Function: This system is activated for prolonged, lower-intensity activities, such as jogging or cycling. It relies on oxygen to produce ATP, making it more efficient for sustained energy production.
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a molecule that carries energy within cells. It’s the body’s immediate source of energy and is needed for explosive movements. When cells use ATP for energy, it converts into adenosine diphosphate (ADP). Creatine sits in our muscles in the form of phosphocreatine. Creatine’s job is to donate a phosphate group to ADP, converting it back into ATP. The more creatine powder or natural creatine you have stored, the longer this process can continue.
Why Take Creatine?
The purpose is for more explosive strength and faster recovery. What is creatine used for in a practical sense? It allows you to do more reps with the same weight.
A common question is: Does creatine help build muscle? Yes. Creatine provides the user with the ability to increase their training volume and load during short bursts of high-intensity exercise. This is helpful for those lifting weights as it allows them to lift heavier or increase repetitions, creating a greater stimulus for growth.
Another frequent question is: Does creatine make you gain weight? Creatine has a cell-volumizing effect where muscle cells hold more water. This gives the tissue a plump, rounded effect that many desire, though it can show slightly on the scale as water weight, not fat. If you do not drink enough water, you can dehydrate, as creatine draws water to the muscles.
Creatine is also widely fed to competing horses and racing pigeons. When horses compete in races or perform Point-to-Point, they too need this explosion of energy.
Who Can Benefit From Using Creatine?
Creatine can be used by everyone. It is particularly beneficial for gym-goers, bodybuilders, weightlifters, and all sportspeople. Creatine powder benefits include increased energy leading to greater training adaptations. The benefit of Ultimate Nutrition supplementation is all about greater output during training sessions, helping you to train longer and stimulate the muscle to a greater effect.

How To Use Creatine - Directions
If you are wondering how to use creatine properly, remember it is important to drink plenty of water. Based on scientific research, it is recommended to take creatine in cycles.
How much creatine should I take?
The typical cycle lasts between 6-12 weeks before taking a break for 2-4 weeks. If you have not used a supplement for over a year, it is recommended to start with a Loading Dose.
Loading Dose
This method is suited to those who want faster results for muscle size, strength & power. Consume 5g, 4 times throughout the day for 5 to 7 days, followed by the maintenance dose.
Maintenance Dose
This method is often preferred for a longer-term supplementation plan. Consume 3-10g per day across 1 to 3 servings.


How to take creatine powder?
The best way to take creatine is by mixing the powder thoroughly with liquid. Regarding when should you take creatine, consistency is key, though many prefer taking it pre- or post-workout. Ultimate Nutrition Creatine is an effective and easy-to-use supplement that can make a real difference to your workouts.
Can Creatine Be Taken With Other Products?
Yes. Creatine can be taken with other products. It can be added to your protein or weight gain shake.
Try it with our Ultimate Nutrition 90+ Advanced Protein or our Professional Whey Protein Isolate, which is Ultra-filtered and Micro-filtered.
It is important to note that the use of Creatine is not restricted by the controlling bodies of any sport.


To Sum Up
The body's energy systems work collaboratively to ensure that we have the energy needed for various physical activities. By understanding how these systems function and utilizing Ultimate Nutrition creatine benefits, individuals can make informed decisions about their training and nutrition to maximize their energy production and overall health.